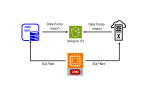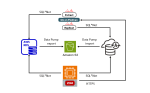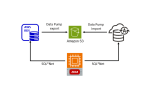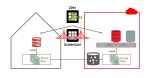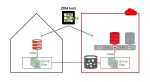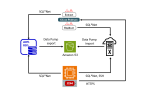
Introduction This blog post describes the steps to migrate from Oracle RDS to Exadata Database Service using Oracle Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) logical online method, which leverages Oracle Data Pump for data export and import and uses Amazon S3 Object Storage to store the Data Pump dump files. Additionally, it uses Oracle GoldenGate to keep…